Recognising Dehydration for a Safe Work Site
Recognising Dehydration Symptoms
Having well hydrated teams minimises risks and accidents in the workplace. Hydration has a direct impact on mood and performance, improving mental clarity and helping with concentration on job tasks.
Being well hydrated has benefits that contribute to the overall health and wellbeing of workers such as promoting kidney function, improving digestion and minimising risks with conditions such as exercise asthma, chronic renal disease, heart disease and stroke. A well hydrated body will be able to regulate body temperature, preventing fatigue which poses many risks on site.
Once the body metabolizes water it needs to be replaced. It provides warning signals for when it needs to be replenished, but many people don’t recognise the signs until it’s too late.
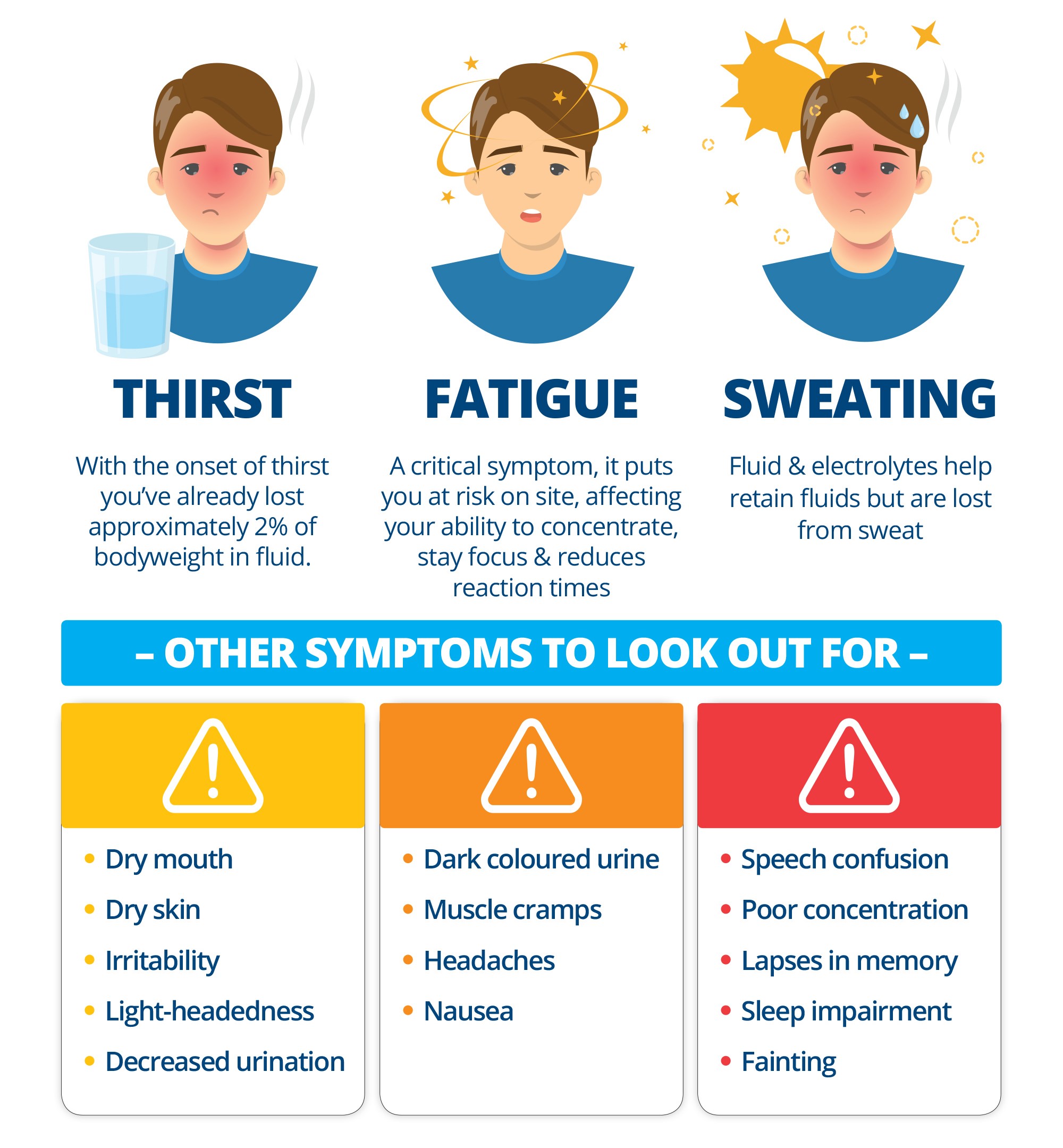
Thirst – Typically the first sign of dehydration is thirst and by this stage it’s too late as you’ve lost approximately 2% of of body-weight in fluid.
Fatigue – One of the most critical symptoms of dehydration is fatigue. When dehydrated blood thickens in the body which puts pressure on the heart as it tries to supply oxygen and nutrients to the body. As a result, the body has to work harder to circulate blood, where muscle weakness and fatigue is experienced. This puts workers at risk as it impacts their ability to concentrate, stay focus and reduces their reaction times.
Sweating – Fluid and electrolytes help retain fluid but are lost when we sweat, which can lead to dehydration. Enough water should be consumed to replace lost water and electrolytes to keep pace with the amount of sweat lost.
Other symptoms to look out for
- Dry mouth
- Dry skin
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Light-headedness
- Decreased urination
- Dark coloured urine
- Muscle cramps
- Speech confusion
- Poor concentration
- Lapses in memory
- Sleep impairment
- Irritability
- Fainting
If symptoms continue without being hydrated it can catch up on workers, escalating to life threatening illnesses such as heat exhaustion, heat stroke or even Hyponatremia.
Hyponatremia is a rare but potentially fatal condition where the excessive consumption of water dilutes blood sodium levels. If someone suffers from this they cannot quench their thirst, regardless of how much water they’ve consumed. Symptoms include headache, nausea vomiting, lethargy and confusion. Weakness and muscle aches and cramps can also be present.
Dehydration can seriously put workers at risk of injury, making them susceptible to errors, dropping tools or stumbling. Dehydration impairs cognitive functions impacting concentration, memory and reaction times. Make sure you and your mates hydrate for a safe work site.









